HMW DNA extraction
Automated High Molecular Weight DNA extraction for Archiving and Long Read Sequencing
Extraction of High Molecular Weight (HMW) DNA (> 100 kb) is currently often performed with manual, time-consuming, and costly methods. As manual workflows are subject to risk of human error and confirm differences in operator handling or laboratory conditions, more time and effort are often required to confirm experimental findings. In worst case scenarios, integrity of samples may compromised.
Seitenmenü
HMW DNA extraction
The chemagic™ nucleic acid purification systems automate the extraction of HMW DNA, improving consistency of results while ensuring sample integrity at higher throughputs and faster turnaround times. Compared with other automated platforms, the chemagic system provided higher DNA yields of good purity alongside a significantly greater HMW DNA extraction efficiency (refer Application Note). The chemagic systems have been used successfully in conjunction with long read sequencing technologies from Oxford Nanopore2,4,5,6 and PacBio1,3. The greater HMW DNA extraction efficiency afforded by chemagic technology also makes it the choice of many biobanks worldwide that require long-term storage stability for archiving and a nucleic acid quality that can be applied to diverse molecular assays2,7,8.
HMW DNA extraction
Key Features
- Efficient automated extraction of HMW DNA at consistent high yields and purities
- Applicable to blood and various sample types with standard chemagic kits
- Fast runtimes with minimal hands-on processing (less pre-preparation steps)
- Proven compatibility with long read sequencing
- Greater long-term storage stability of isolated nucleic acids
- Further size selection applicable with M-PVA Magnetic Beads
HMW DNA extraction
Webinars
Webinars
March 27th, 2024 - Available on demand
In this talk, Karine Auribault from Hôpital Européen Georges-Pompidou in Paris will share her experience implementing an automated DNA extraction method with the chemagic 360 instrument in the hospital’s routine genetic testing research workflows. Data showcasing various assays such as multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA), Sanger sequencing, NGS including targeted sequencing, multiplex PCR, and long read sequencing with Oxford Nanopore will be shared.
Webinars
April 18th, 2024 - Available on demand
Here, Emily Farrow from Children’s Mercy Hospital in Kansas will share her experiences in clinical research where laboratories often utilize several different assays in their testing process. Particularly in pediatrics, leveraging a single high throughput DNA isolation method is critical to enabling testing and method development. This webinar will discuss the implementation of an automated DNA isolation protocol; DNA quality and quantity metrics, and the impact on downstream assays, such as long read NGS.
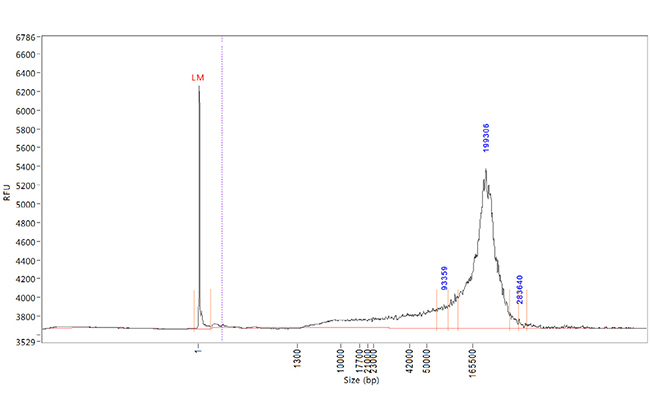
Efficient HMW DNA extraction for Leong Read Sequencing
Efficient HMW DNA extraction for Long Read Sequencing
Extraction performance from blood based on DNA yield, purity, and integrity was compared between two automated nucleic acid extraction systems.
Reliable partner for population genetic cohort studies in Biobanking
Drawing on extensive expertise in high-throughput extractions across diverse sample types such as blood, buffy coat, swabs, and saliva, we have established a global presence in biobanking. Our chemagic nucleic acid isolation ensures archive-quality specimens, and our ability to automate entire workflows, from primary sample handling to downstream QC and assay setup, has positioned us as a trusted collaborator in various population genetic cohort studies.
Our contributions extend to notable initiatives like the "All of Us Research Programme" from the Mayo Clinic7, the German National Cohort/NAKO Gesundheitsstudie8, and the British Initiative, including the 100,000 Genomes Project, among others.
Contact us
Contact us
Our specialists have over 25 years’ experience in automated nucleic acid purification from diverse sample types and its implementation in laboratories of all sizes and application areas. If you would like a FREE consultation with a technical expert on automated HMW DNA extraction, please fill in this form with your details and specific question(s):
References
References
- Lang K, Wagner I, Schöne B, et al. ABO allele-level frequency estimation based on population-scale genotyping by next generation sequencing. BMC Genomics. 2016;17:374. Published 2016 May 20.
- Beyter D, Ingimundardottir H, Oddsson A, et al. Long-read sequencing of 3,622 Icelanders provides insight into the role of structural variants in human diseases and other traits. Nature Genetics. 2021 Jun;53(6):779-786.
- Steiert TA, Fuß J, Juzenas S, et al. High-throughput method for the hybridisation-based targeted enrichment of long genomic fragments for PacBio third-generation sequencing. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2022;4(3):lqac051. Published 2022 Jul 13.
- Schmidt J, Berghaus S, Blessing F, et al. Genotyping of familial Mediterranean fever gene (MEFV)-Single nucleotide polymorphism-Comparison of Nanopore with conventional Sanger sequencing. PLoS One. 2022;17(3):e0265622. Published 2022 Mar 17.
- Watson CM, Crinnion LA, Hewitt S, et al. Cas9-based enrichment and single-molecule sequencing for precise characterization of genomic duplications. Lab Invest. 2020;100(1):135-146.
- Watson CM, Crinnion LA, Simmonds J, Camm N, Adlard J, Bonthron DT. Long-read nanopore sequencing enables accurate confirmation of a recurrent PMS2 insertion-deletion variant located in a region of complex genomic architecture. Cancer Genet. 2021;256-257:122-126.
- Valentin N, Camilleri M, Carlson P, et al. Potential mechanisms of effects of serum-derived bovine immunoglobulin/protein isolate therapy in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Physiol Rep. 2017;5(5):e13170.
- Kousathanas A, Pairo-Castineira E, Rawlik K, et al. Whole-genome sequencing reveals host factors underlying critical COVID-19. Nature. 2022;607(7917):97-103.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.