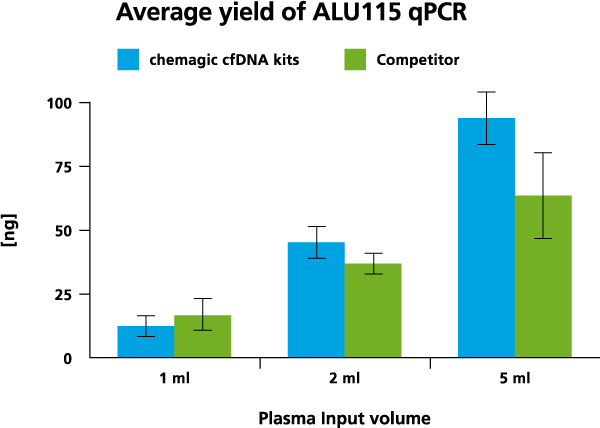High yields with chemagic™ automated or manual purification of circulating cell free DNA
Circulating cell free DNA (cfDNA) in body fluids is being used for noninvasive, real-time biomarker research and more. Yet detection is often challenged by its low levels, fragmentation and preanalytical variabilities introduced by sample collection, plasma preparation, and nucleic acid purification.
Revvity chemagic cfDNA isolation kits, together with dedicated chemagic instruments rely on patented chemagic technology using M-PVA Magnetic beads to ensure a high quality of nucleic acid purification. Comparable yields to manual spin column methods were obtained with efficient removal of contaminants and exclusion of cross-contamination. With automation, variabilities associated with multiple handling steps are reduced and sample integrity maintained with full sample tracking capabilities.
Features
Benefits of automated cfDNA isolation with chemagicTM technology:
- Reliable and comparable yields to manual methods
- Fast, automated workflow with on-board lysis and no heating required
- Wide range of sample inputs applicable from 0.5 to 18 ml
- Full sample tracking with barcode reading and bidirectional LIMS communication capability
- Ability to isolate viral nucleic acids
- Suitable for fresh or frozen plasma/serum from EDTA, citrate or Streck® Cell-free DNA BCT® tubes
- Downstream compatibility with various assays - ddPCR, NGS, qPCR etc.
- Compatibility with other automated Revvity systems
Application data
cfDNA isolation was done from 1 ml, 2 ml, and 5 ml from two different donors both with the chemagic kits on the chemagic 360 instrument and manually with competitor. For cfDNA analysis, a short fragment (115 bp) from a consensus sequence with abundant genomic ALU repeats was amplified. The exemplary data from donor 2 shows that the yield of cfDNA is scalable to sample input.
Customer Review
Customer Review
“The chemagic™ cfDNA extraction kit on the chemagic 360 platform has greatly reduced the hands-on time needed for sample preparation. It has also given us improved cfDNA yields compared to the current, manual approach used in our laboratory and enabled significantly higher throughput. The ease-of-use of the system is high and has made it easy for us to rapidly train our staff and implement the approach in our day-to-day practice.”
Veli-Mikko Puupponen, CEO, BiopSense Oy/Ltd, Finland
“We use cfDNA extracted with chemagic™ technology in digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) assays to support diagnosis of colorectal cancer (Calleson et al., 2022), lung cancer (Frank et al., 2022) and anal cancer (based on HPV cfDNA detection, Lefèvre et al., 2021) with a sample to result turnaround time of 48 h.”
Professor Niels Pallisgaard, Dept of Pathology, Zealand University Hospital, Denmark
Webinar
Webinar
Webinar
The webinar focuses on optimization of the analytical steps including sampling, plasma isolation and purification (yield, degree of single stranded DNA, Proteinase K carryover and elution volume). Setup of ctDNA dPCR with dPCR assay controls, number of replicates and sample QC controls are discussed, including use of spike-in, measurement of contaminating lymphocyte DNA and DNA fragmentation. Strategies to select the optimal dPCR assay, identify germlines mutations, CHIPs and patients that are ctDNA non-shedders are presented. Finally, different ways to report ctDNA graphically are shown with pros and cons discussed.
Looking for a Manual Option?
If you do not have a chemagic instrument but would like to benefit from the advantage of chemagic M-PVA Magnetic Bead technology, the manual chemagic cfDNA 5k kit is now available. Process up to 5 ml of sample and avoid spillages and clogs linked to spin column or vacuum-based systems with an easy magnetic bead-based protocol.

Manual cfDNA extraction with chemagic cfDNA 5k kit
Specifications:
- 40 preps
- 1-5 ml plasma/serum input
- 30-100 µl elution volume
- 60-90 minutes processing time
Additional magnetic racks required, see Product Overview for Manual DNA Isolation for details
Plasma Preparation Protocol
Product overview for Automated cfDNA isolation
| Catalog No. | Kit Name | Instrument | Samples/Batch | Preps/Kit | Sample Volumes | Processing Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMG-1444* | chemagic Prime™ cfDNA 5k Kit H24 | chemagic Prime 4/8 | 24 | 240 | 3 - 5 ml | 240 min |
| CMG-1304* | chemagic cfDNA 5k Kit H24 | chemagic 360/MSM I | 24 | 240 | 3 - 5 ml | 100 min (incl. 15 min hands-on time) |
| CMG-1302* | chemagic cfDNA 2k Kit H24 | chemagic 360/MSM I | 24 | 240 | 1 - 2 ml | 90 min (incl. 15 min hands-on time) |
| CMG-1310* | chemagic cfDNA 10k Kit H24 | chemagic 360/MSM I | 24 | 240 | 6-10 ml | 115 min (incl. 20 min hands-on time) |
| CMG-1318 | chemagic cfDNA 18k Kit H12 | chemagic 360/MSM I | 12 | Up to 250 | 10, 15 or 18 ml | 125 min (incl. 15 min hands-on time) |
| CMG-1396 | chemagic cfDNA 1.5k Kit H96 | chemagic 360/MSM I | 96 | 960 | 0.5 - 1.5 ml | 120 min (incl. 30 min hands-on time) |
*Additional accessories required: 3 quantity chemagic 13 mL Double Bottom Rack H24 (art. No. CMG-13005340)
Product overview for Manual cfDNA isolation
| Product No. | Kit Name | Accessories required Preps / Kit | Sample Volumes | Processing Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMG-134 | chemagic™ cfDNA 5k Kit | chemagic™ Stand 2 x 12 chemagic Magnetic Stand Type F chemagic cfDNA Stand 12 (Optional) | 1 - 5 ml | 60-90 min (depending on user experience) |
Plasma Preparation Protocol
Best Practices in cfDNA Purification
Sample Collection & Plasma Preparation
To avoid contamination of cfDNA with genomic DNA from ruptured blood cells, it is recommended to prepare plasma as fresh as possible (within 24h after blood draw for EDTA tubes or longer for specialized cell free blood collection tubes, refer to tube manufacturer).
A double centrifugation protocol during plasma preparation is recommended to minimize the potential carry over of cells and genomic DNA (refer to tube manufacturer for max. centrifugation speeds). Special care should be taken to avoid transfer of any other blood components (buffy coat or red blood cells) when separating the plasma fraction.
From 10 ml of whole blood, approximately 4 - 5 ml plasma can be expected. For a guidance on how to prepare plasma for cfDNA analysis, please refer to manuals below.
cfDNA Quantification
cfDNA yields isolated from human plasma samples are typically in the range of 1 - 30 ng/mL of plasma and therefore critically low and maybe outside the detection parameters determined by spectrophotometric methods. If quantification of the extracted cfDNA is required, two methods are recommended: A PCR-based method (qPCR, ddPCR) and a fragment analysis assay where an internal reference is used such as Labchip cfDNA Assay. Quantification based on fluorometric method may lead to varying results dependent on various factors and therefore is not recommended. Likewise, fragment analysis methods based on upper marker peak size will lead to inaccurate quantitation and should be avoided. Please refer to manuals for more details.
Download Manual
| Catalog No. | Kit Name | PDF Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| CMG-134 | chemagic™ cfDNA 5k Kit (manual) | Protocol CMG-134 chemagic cfDNA 5k Kit |
| CMG-1304 | chemagic™ cfDNA 5k Kit H24 | Protocol CMG-1304 chemagic cfDNA 5k Kit H24 |
| CMG-1302 | chemagic™ cfDNA 2k Kit H24 | Protocol CMG-1302 chemagic cfDNA 2k Kit H24 |
| CMG-1396 | chemagic™ cfDNA 1.5k Kit H96 | Protocol CMG-1396 chemagic cfDNA 1.5k Kit H96 |
| CMG-1310 | chemagic™ cfDNA 10k Kit H24 | Protocol CMG-1310 chemagic cfDNA 10k Kit H24 |
Application Notes
Contact us for further information
References
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.