Human genetic testing
Human genetic testing - reliable performance in diverse assays
The increasing demand for high quality nucleic acids to meet the growing assay diversity in human genetic testing has driven the use of automation. chemagic™ automated nucleic acid purification has the unique ability to process large sample volumes to achieve archive-quality nucleic acids. It has been used for diverse applications including HLA genotyping for donor screening, MLPA for cancer testing, NGS from dried blood spots for newborn screening, digital PCR from cfDNA-based liquid biopsies for personalized medicine and more. With CE-IVD certified kits as well as customized kits to fit specific needs, Revvity solutions help achieve the flexibility and efficiency required for every workflow.
Where our products are used:
- Clinical genetics and molecular diagnostic laboratories including hospitals and service labs
- Donor screening institutions
- Biobanks
- Pharmaceutical/biotech/CRO
- Government and Academic Research Laboratories
Features
Key Features
- Archive-quality nucleic acids compatible with diverse downstream applications e.g., HLA typing, MLPA, NGS, etc.
- Ability to cater kit requirements to workflow
- Automation for time-savings, sample tracking and consistent performance with minimized down time
- High sample volume and throughput flexibility
- Affordable running costs
- CE-IVD certified kits
Customer Review
Review
“More than 10 years ago, we chose chemagen instruments and reagents for isolating DNA from blood or buccal swabs. After performing HLA genotyping on over 10 million samples, we remain extremely satisfied with this decision and the consistent performance.”
Vinzenz Lange, DKMS Life Science Lab, Germany
Product Overview for IVD compliant workflows
| Product No. | Kit Name | Instruments | Format | Preps/Kit | Sample Volume | Sample Material | Processing Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVD-1091* | chemagic™ BBS DNA Kit H96 | chemagic 360 instrument chemagic Prime™ instrument | 96 well | 960 | 400 µl | Blood, buffy coat, saliva | 79 min |
| IVD-1074* | chemagic™ BBS DNA Kit H24 | chemagic 360 instrument chemagic Prime™ | 24 well | 240 | 2-4 ml | Up to 4 ml blood, saliva, up to 2 ml buffy coat | 78 min |
| IVD-704* | chemagic™ BBS DNA Kit H12 | chemagic 360 instrument chemagic Prime™ | 12 well | 250 | Up to 10 ml | Up to 10 ml blood, up to 4 ml saliva, up to 2 ml buffy coat | 78 min |
*Products may not be licensed in accordance with the laws in all countries, such as the United States and Canada. Please check with your local representative for availability.
View other kits here:
- DNA and RNA from Blood
- DNA and RNA from Saliva
- DNA and RNA from Buffy Coats
- DNA and RNA from Buccal Swabs
- DNA from Dried Blood Spots
- DNA and RNA from other samples
- cfDNA isolation
- microRNA isolation
DNA and RNA for genetic testing
Workflows
DKMS Life Science
High-throughput HLA Typing at DKMS Life Science Lab, the World’s Largest Stem Cell Donor Register
With a mission of matching suitable donors to patients with blood cancers and blood disorders, DKMS Life Science Lab has employed high end automation to process up to 1 million samples per year. Read more about their experience performing HLA genotyping from buccal swabs with an NGS-based amplicon approach1.
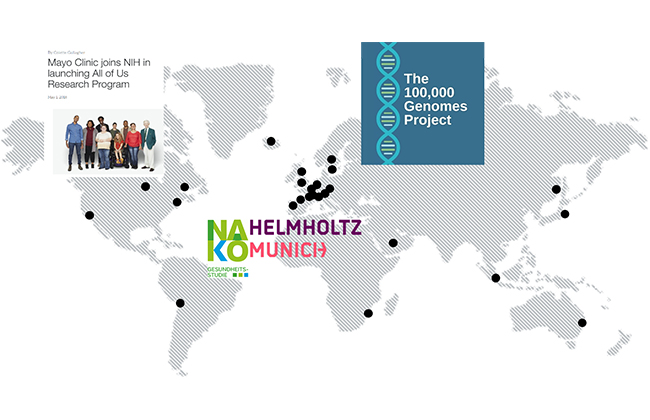
Trusted Biobanking Partner in Population Genetic Cohort Studies
Our vast experience in high throughput extractions from different sample types (e.g., blood, buffy coat, swabs, and saliva) has helped us establish a global footprint in biobanking.The archive-quality of chemagic nucleic acid isolation coupled with our capability for automating full workflows from primary sample handling down to downstream QC and assay setup has made us a trusted partner in various population genetic cohort studies.
These include the “All of Us Research Programme” from the Mayo Clinic2, German National Cohort/NAKO Gesundheitsstudie and the British Initiative, 100 000 genomes project3 amongst others.
Large Volume DNA Extractions for MLPA, Long-range PCR and Sequencing
Genetic studies typically require multiple testing from the same sample to corroborate findings or to complement primary assay results. The unique large sample volume processing capability of chemagic instruments, attributed to the flexible interchangeable rod head system, therefore helps laboratories to maximize yield and efficiency. Large volumes (5 ml) of whole blood are were required to obtain sufficient DNA for the multiple genetic tests done at the Erasmus MC that include MLPA, Denaturing Gel Electrophoresis (DGE), Long-range PCR, and Sequencing.
Automated Purification of High Integrity RNA for RNA-Seq
The chemagic RNA isolation technology has been applied to various sample types including blood, tissues, cells and other body fluids, and has provided researchers consistent high integrity RNA suitable for a variety of downstream applications including RNA sequencing4. Low and high volume RNA extractions have also been successfully performed from a variety of different blood collection tubes such as PAXgene® Blood RNA Tubes and S-Monovette® RNA Exact from SARSTEDT.

High-quality, NGS-grade DNA and RNA from FFPE Tissues for Personalized Medicine
With chemagic technology, you can avoid the use of organic solvents with an optimized heat treatment step or ultrasonic disruption with Covaris technology. High quality chemagic nucleic acid extraction from FFPE tissues has been successfully applied in Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) to detect mutations and epigenetic changes, contributing to a deeper understanding of diseases and guiding personalized therapeutic approaches5,6,7.

NGS-grade DNA Isolation from Dried Blood Spots
Dried blood spots require low blood volumes (30-100 μL per spot), are easy and cost-effective to collect, transport and store and are used in newborn testing13, diagnostics and drug level monitoring. The chemagic™ extraction from DBS (3 to 13 mm punchout) typically yields 0.5-2 µg high quality genomic DNA that has been validated with NGS including linked-read sequencing applications and can be applied for low to high throughputs, suitable for laboratories of any size or stage of development.
High yield scalable cfDNA extractions from liquid biopsies for diverse applications
The application of cfDNA extraction from liquid biopsies holds promise across a spectrum of disciplines, from cancer diagnostics to prenatal testing, offering the potential for early detection and personalized therapeutic interventions. With chemagic cfDNA extraction, labs can easily scale from manual to automated workflows using the same M-PVA Magnetic Bead chemistry for sample volumes up to 18 ml. High and consistent yields have been obtained with proven performance in diverse downstream assays including digital droplet PCR, NGS, or qPCR.
Automated purification of microRNA for small RNA sequencing
Extraction of circulating miRNAs are challenged by low concentrations, small sizes and association with protein complexes. The automated chemagic extraction technology provides a fast, automated workflow that has been validated with various downstream assays including Revvity’s NEXTFLEX® Small RNA-Seq Kit v4 that enables gel-free small RNA library preparation. Reliable performance and a high diversity of miRNAs were observed from sequencing results.
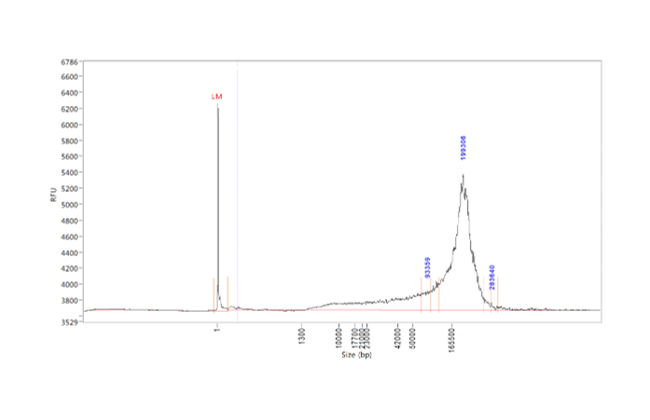
Efficient HMW DNA extraction for long read sequencing
Current high molecular weight (HMW) DNA extraction methods are mostly manual, time-consuming and costly. Inconsistent results often arise from differences in operator handling or laboratory conditions.
chemagic standard extraction kits obtain HMW DNA with fragment lengths ranging up to ~200 kb dependent on sample material and have been successfully applied to Oxford Nanopore8,9,10 and PACBIO11,12 long read sequencing platforms.
DNA and RNA for genetic testing
Resources
DNA and RNA for genetic testing
References
- Schöfl, Gerhard et al. “2.7 million samples genotyped for HLA by next generation sequencing: lessons learned.” BMC genomics vol. 18,1 161. (2017)
- Valentin, Nelson et al. “Potential mechanisms of effects of serum-derived bovine immunoglobulin/protein isolate therapy in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome.” Physiological reports vol. 5,5 (2017)
- Kousathanas, Athanasios et al. “Whole-genome sequencing reveals host factors underlying critical COVID-19.” Nature vol. 607,7917 (2022)
- Schieck, Maximilian et al. “Implementation of RNA sequencing and array CGH in the diagnostic workflow of the AIEOP-BFM ALL 2017 trial on acute lymphoblastic leukemia.” Annals of hematology vol. 99,4 (2020)
- Sorrells, Shelly et al. “Longitudinal and multi-tissue molecular diagnostics track somatic BRCA2 reversion mutations that correct the open reading frame of germline alteration upon clinical relapse.” NPJ genomic medicine vol. 6,1 17. 22 Feb. (2021)
- Benhamida, Jamal K et al. “Reliable Clinical MLH1 Promoter Hypermethylation Assessment Using a High-Throughput Genome-Wide Methylation Array Platform.” The Journal of molecular diagnostics : JMD vol. 22,3 (2020)
- Magnusson, Magnus I et al. “Histopathology and levels of proteins in plasma associate with survival after colorectal cancer diagnosis.” British journal of cancer, 10.1038/s41416-023-02374-z. 18 Aug. (2023)
- Beyter, Doruk et al. “Long-read sequencing of 3,622 Icelanders provides insight into the role of structural variants in human diseases and other traits.” Nature genetics vol. 53,6 (2021)
- Watson, Christopher M et al. “Cas9-based enrichment and single-molecule sequencing for precise characterization of genomic duplications.” Laboratory investigation; a journal of technical methods and pathology vol. 100,1 (2020)
- Watson, Christopher M et al. “Long-read nanopore sequencing enables accurate confirmation of a recurrent PMS2 insertion-deletion variant located in a region of complex genomic architecture.” Cancer genetics vol. 256-257 (2021)
- Lang, Kathrin et al. “ABO allele-level frequency estimation based on population-scale genotyping by next generation sequencing.” BMC genomics vol. 17 374. 20 May. (2016)
- Steiert, Tim Alexander et al. “High-throughput method for the hybridisation-based targeted enrichment of long genomic fragments for PacBio third-generation sequencing.” NAR genomics and bioinformatics vol. 4,3 lqac051. 13 Jul. (2022)
- Balciuniene, Jorune et al. “At-Risk Genomic Findings for Pediatric-Onset Disorders From Genome Sequencing vs Medically Actionable Gene Panel in Proactive Screening of Newborns and Children.” JAMA network open vol. 6,7 e2326445. 3 Jul. (2023)
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.



